Which Term Best Describes Rewarding Successive Approximations Of A Target Behavior?
So, when it comes to which term best describes rewarding successive approximations of a target behavior?
The answer to the question is Shaping. This is a technique when someone is trying to achieve the desired behavior. And this term is also called reinforced. But, on the other hand, if there are no approximations in the behavior, then there is no reinforced. In this article, you will learn everything about positive and negative punishment, reinforcements, and general psychology textbooks.
Which Term Best Describes Rewarding Successive Approximations Of A Target Behavior?
When it comes to the topic, there are a couple of things that you must know. The first thing is shaping. So, in simple words, shaping is a technique to achieve the desired behavior. Other than this, there are a couple of other things that you must know. These terms are- Operant Conditioning, Behaviorism, and Perspectives.
Operant Conditioning: What Is It And How Does It Work?

The term is also called instrumental conditioning. So what is it?
So, im simple words, it is a learning method. The method determines the probability of consequences. And these consequences are the response of a subject. Through this method, reinforced can be repeated. And the behavior occurs less frequently. If you find the history of operant conditioning, you will see that the psychologists behind the theory were John B. Watson and B.F. Skinner.
Skinner believed that human minds are beyond many things. So he started to observe the behavior. And he believed that behavior is more productive than internal mental events. His work is also called classical conditioning, and he elaborated the theory simply that it consists of complex human behavior. This is operant conditioning.
He is the father of Operant Conditioning. Excluding the experiments, he also talked about Reinforcement behavior. He also extinguished the repeated behavior, which is not a reinforced behavior. In 1948, he conducted an experiment by using animals and placing them in the Skinner Box.
Skinner Box
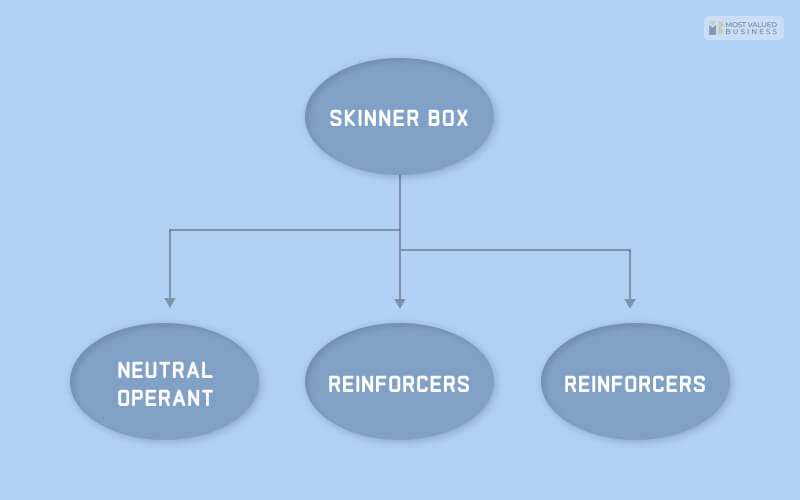
The skinner box or the operant conditioning chamber is a box where he could observe and then record an animal’s behaviors in a specific time frame. There are two different tests. One is where the animal will get a reward, and one is where the animal will get punishment for certain behaviors. He chose lever pressing for rats and key pecking for pigeons.
While conducting this experiment, there were three different responses that he found.
Neutral Operant
As you can see, the term neutral, he got neutral results in the probability of repeated behavior. The behavior neither increased nor decreased.Reinforcers
The environmental responses increased the repeated behavior. He saw that the reinforcers increased, and the result was either positive or negative.Punishers
The environmental responses decreased the repeated behavior. The result was the opposite of the reinforcers, and, most importantly, the behavior got weak for the punishment.
Reinforcement And Punishment: Examples
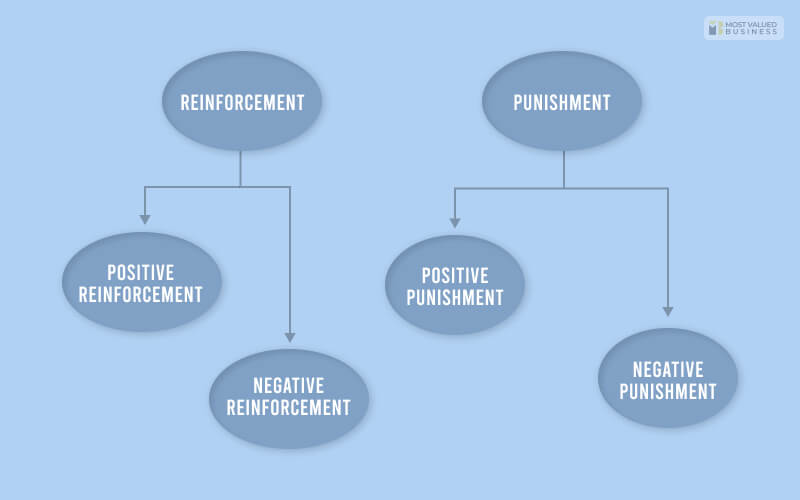
I know that the topic is not easy to understand. So here are the four different aspects with examples so that you will understand the topic. You will also understand positive vs negative reinforcement.
Before starting, you must know positive means adding something, and negative means removing something. You will get to learn reinforcers have innate reinforcing qualities from these examples.
1. Positive Reinforcement
This means there must be something adding. And the adding is to increase the behavior. Let an example of a gym. Suppose the trainer of the gym has added yoga at the end of the gym, and everyone needs to do that. So this is a scenario where adding yoga will increase the behavior.
2. Negative Reinforcement
This means there will be something is taking away. And reinforcement is to increase the behavior. Let’s take the same example. Suppose the trainer implements a new rule to do 50 push-ups at the end of a session. But there is a lack of interest. So he made that 25 push-ups. And this action made people increase their behavior. So, here taking away something is increasing the behavior.
3. Positive Punishment
As I have already said that positive means adding something. And the punishment is to decrease behavior. For example, suppose the trainer has found that most people use their mobile phones while working out. So, he makes a rule if somebody is caught using a mobile phone, then they have to sprint to the end of the gym. Here adding the sprint decreased the use of the mobile phone. So, it is a positive punishment.
4. Negative Punishment
In this case, the first thing is to take something away. And the purpose is to decrease the behavior. The same gym trainer sees that people do not follow the proper way to work out. Instead of that, they are doing everything wrong. So, he decided that there would be no yoga. So, removing yoga will make them focus on the current equipment. I hope you get to learn negative punishment psychology definition.
Frequently Asked Questions!!! (FAQs):
Here are some important questions and answers.
Ans: Children do not know how to develop behavior, so teachers use shaping procedures to teach them and develop behaviors. Then, they use successive approximations to achieve the desired final behavior. The approximations are close to the required behavior. So teachers need to extinguish between behaviors.
Ans: When Skinner did the experiments on operant conditioning, he used the term shaping. This is an approach that of more rewarding. Here, he gave rewards to target behavior after successive approximations.
Ans: The successive approximations method, or the SAM, is also called one of the classical methods when it comes to solving integral equations. Another name of the method is the Picard iteration method. You will find the term in literature. You will also find a scheme that a person can use for initial value problems or integral equations.
Final Words
I hope now you have understood which term best describes rewarding successive approximations of a target behavior.
For a small test, if I ask you, Which of the following is an example of positive punishment? If you can give examples of a couple of incidents, then you are on the right path.
If you still have any questions, please let us know in the comment section below.
Thank You.
Read More:



